Evaluation the outcome of urological phone consultation during COVID-19 pandemic
Waleed Shabana1, Neda Ghaffari-Marandi1, Emmanuel Kawa1, Mohammed Bassuony1, Ahmed Kotb1, Hazem Elmansy1, Walid Shahrour1.
1Northern Ontario School of Medicine, Thunder Bay, ON, Canada
Introduction: We aim to assess patient satisfaction of conversion to phone consultation in urology clinic during COVID-10 pandemic and to investigate potential patients’ complaints that could be handled in the future as phone consultation.
Methods: A retrospective review for new urological teleconsultation between April 2020 and September 2020 in our institute.A telephonic interview was conducted with potential participants who were invited to answer a designed questionnaire.The questionnaire included 9 questions covering patient satisfaction,quality of educational information,confidentiality, ability to share sensitive information,efficacy in absence of physical examination,overall acceptance, and preference of future teleconsultation regarding time and cost saving.Patients' responses scaled using a five-point Likert scale (1 =strongly disagree - 5 = strongly agree).
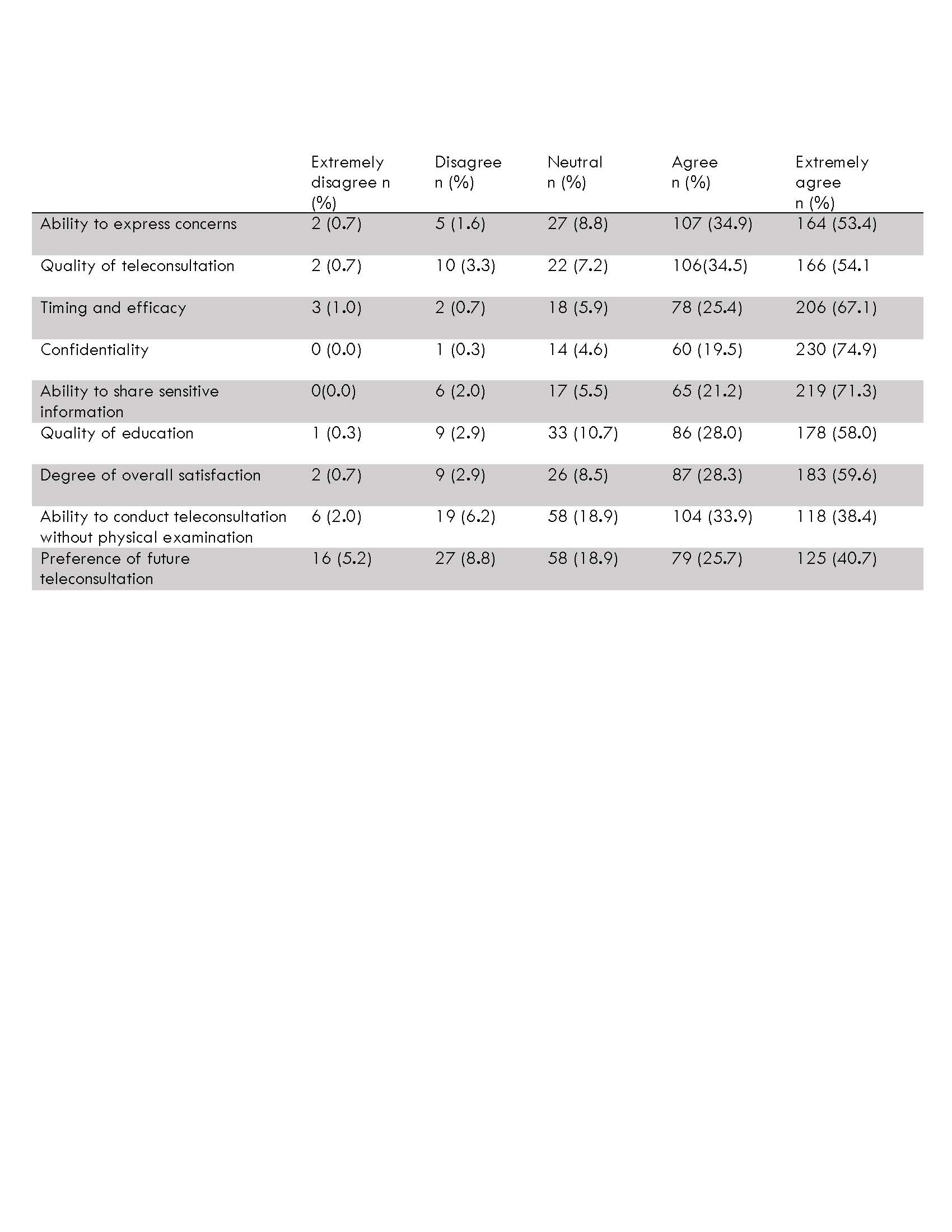
Results: After screening and assessment, 770 out of 864(89.1%) patients fulfilled the inclusion criteria. 94(10.9%) were excluded due to hearing impairment,or age under 18. 42 (5.5%) refused to participate,310 (40.3%) of the patients could not be reached by phone and eventually only about307(39.9%) completed the questionnaire.The highest percentage of agreement (94.4%) was among those who felt consultation was private and confidential. The lowest agreement was found in the question relating to the ability of the physician to do the job without physical exam (72.3%). A total of 204 (66.4%) patients agreed to future teleconsultation regarding time and cost savings. On multivariate analysis, irritative lower urinary symptoms was the only independent factor associate with high degree of satisfaction (p=0.02) and wish for future teleconsultation (p=0.03).
Conclusions: Urological teleconsultation is a feasible option during travel restrictions as in COVID-19 pandemic. Two thirds of patients agree for future teleconsultation. For one third of patients, the inability to perform physical examinations is a concern.